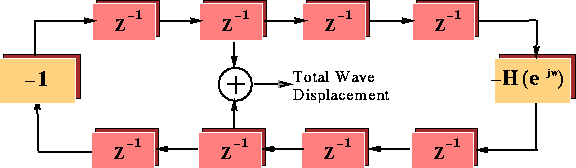
Figure 2: The Basic Construction of a Digital Waveguide Network
A large body of research in the last few years has given rise to efficient sound synthesis techniques that are based on physical models of sound generating systems, [3]. These models are oftwen called waveguide models in the literature.
The basic elements of a waveguide model are the left and right traveling components of the wave equation. When implemented using techniques from Digital Signal Processing, the numeric values contained at each of the defined nodes in the system are exactly equivalent to the spatially sampled numeric solution to the wave equation. This relates the digital signal processing system to the underlying physics of the acoustic system by an isomorphism\

Figure 2: The Basic Construction of a Digital Waveguide Network
The waveguide technique of solving the equations is efficient thus allowing real-time implementation on a microcomputer workstation. Figure 2 shows the basic construction of a waveguide physical model built from delays and filters.\
We used waveguide models of a trumpet and a saxaphone for our modeling experiments. Each model had four degrees of freedom that were estimated by the inverse model function approximator.