The training set for the forward model comprised pairs of
action parameters and sound outcomes. We used the same non-convex
training set as for the direct inverse model but with the inputs and
outputs reversed. Once learned, the forward model was able to
approximate the input/output behavior of the physical model.
The output of the forward model is called the predicted
outcome ![]() and the difference between the sound intention
and the difference between the sound intention ![]() and the predicted outcome
and the predicted outcome ![]() is the
predicted performance error:
is the
predicted performance error:
We used this error for optimizing the forward model.
As in the two previous experiments, the forward model was implemented as a
two-layer feed-forward network with 2 linear units for inputs,
representing string selection and stop positions, 20 logistic hidden
units and 61 output units
corresponding to the sample estimates of the violin string models.
The forward model was trained until the predicted performance error reached an
accuracy of ![]() bits, (mean-squared predicted performance error
bits, (mean-squared predicted performance error ![]() ). Figure
). Figure  shows the convergence of the forward model
to within the chosen treshold. The lower graph in
figure
shows the convergence of the forward model
to within the chosen treshold. The lower graph in
figure  shows the mean-squared predicted performance
error for each of the training patterns. \
shows the mean-squared predicted performance
error for each of the training patterns. \
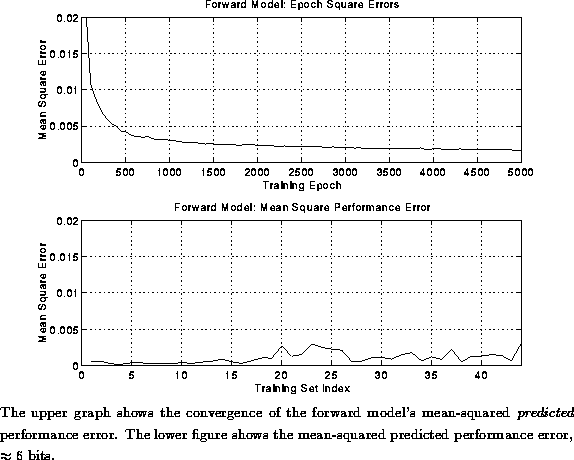
Figure: Convergence and Mean Errors of Forward Model
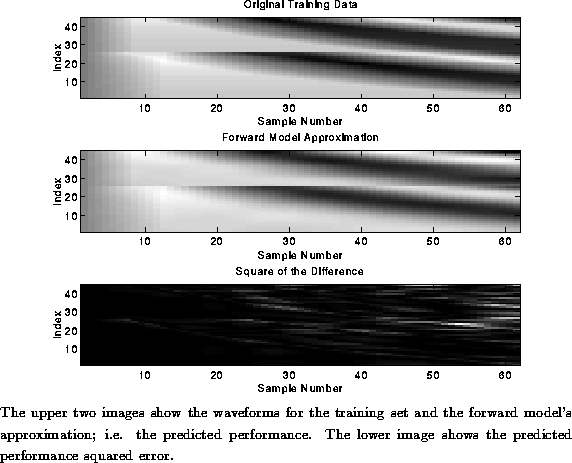
Figure: Predicted Performance Outcome of Forward Model