
Model-based audio is a sound representation that is essential for large-scale networked applications such as Virtual Worlds and mobile internet music distribution. My Ph.D. thesis explored the use of information theory and sound analysis techniques to create general sound synthesis techniques that offer controllable audio for use in networked interactive applications and network distribution of audio.
We have built a transport mechanism for sound that requires only a signal processing network specification and an event list to drive it. This results in an extremely low bandwidth representation for music.
NetSound Page[HTML] ICMC96 NetSound Paper[HTML]

Current interactive media and VR applications use head-mounted stereo headphones and microphones to perform audio capture, for speech recognition, and rendering 3D audio. This project explores the use of adaptive algorithms for beamforming and for steerable 3D audio. We have built a system that does not use body-mounted equipment for the Media Lab's IVE system.
AES99 Preprint #4052 (B-2)[PostScript 2312K] [HTML version]

A system that supports many users interacting in the same environment creating sound and animated graphics using a gesture interface.

I have been working with Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories on a large-scale multi-user scalable virtual reality operating environment called SPLINE. A large-scale virtual environment has been implemented called Diamond Park which is the first SPLINE application. SPLINE and Diamond Park were shown at COMDEX in Las Vegas, November 13-17 1995.
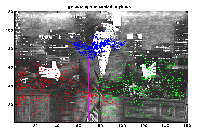
Standup comdedians make great human gesture data. The gesture delivery is practiced and timed to maximize the impact on the audience. We have built a system that extracts audio and visual features from recorded video data and classifies these features using unsupervised clustering techniques.
The data is recorded segments of Jay Leno's "Tonight Show" and David Letterman's "Late Show". The goal is to create tools for browsing video databases for segments that would be of interest to viewers.
[Postscript (0.9Mb)] [Frame Maker (1.9Mb)] [HTML version]
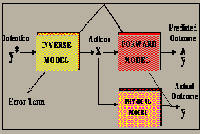
We are implementing a system that uses competition among parallel sound models in order to classify sounds and estimate various salient parameters for each model. Our research comprises exploring robust parameter estimation techniques for various sound models.
[Connection Science 6:2&3, pp. 355-371, 1995] [HTML version]