



Previous: Internal Interface
Up: Data Structures
Next: Predefined Parameter Types
The structure for representing the parameters has several requirements:
- It should identify the type of data being passed, to allow for
translation between its standard format and the format desired by the
stream processor selected for execution.
- It should support parameters with large bit sizes (up to 64
bits, at least.)
- It should be compact, to minimize transmission latency over slow
communications channels.
These requirements strongly suggest the use of a tagged, variable
length data word to represent each parameter. To simplify the
software task of translating the standard format into the processor
specific one, the size of the data word must be a multiple of eight
bits (referred to hereafter as a byte.)
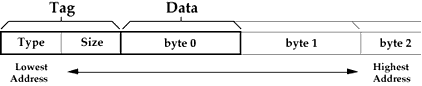
Parameter Word Representation
The first byte of the parameter word is a tag containing both a four
bit parameter type field, and four bits indicating the number of bytes
of data in the parameter word. The parameter words are located in
memory with the byte containing the tag in the lowest memory address,
following by the least significant byte of the data word in the next
higher address.
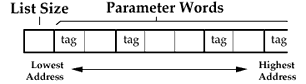
Parameter List Representation
The parameters are passed as a list, started with a size field
specifying the number of bytes in the parameter list (not including
the size field). The size field utilizes one byte, limiting the
parameter list to at most 255 bytes of parameters. This allows
up to fifty 32-bit parameters, or fifteen 128-bit parameters, to be specified.
magiceight-web@media.mit.edu


