 X Forwarding
X Forwarding
NOTICE:
This is not the only way of doing X Windows Forwarding. Here we use two open-source programs: Putty and Xming (a "X-Window Server").
Alternatives:
- There is also an alternative tutorial based on Putty and Cygwin, you can find it at http://www.cs.dartmouth.edu/~bmeister/putty-cygwin-tutorial.pdf
- Dartmouth has license for another program "Reflection-X" that basically does the same thing. You can download it from here.
- You can also perform the same task with Cygwin only. But we will
not cover Cygwin here since it is quite a big and different topics.
STEP ONE: Install Putty and Xming.
You can get the Xming installation package here.
STEP TWO: Configure and Start Xming.
Run Xming through Start->Programs->Xming->Xming. The first time you do this, you may see some configuration window.
Do as follows:
- Choose "Multiple Window"
- Choose "Start no client"
- Rest use the default option.
Ok. When you've done all that, you will only see a small ICON on the task bar like this.  The first ICON is the Xming process.
The first ICON is the Xming process.
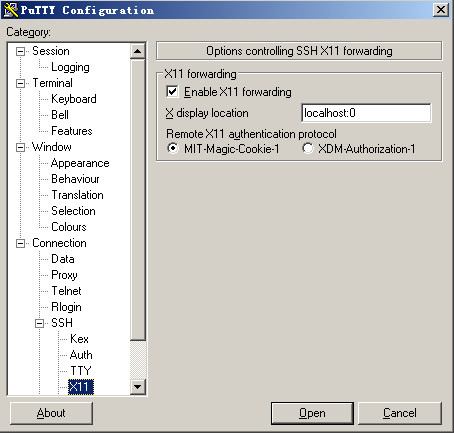
STEP THREE: Configure Putty
To use X-Forwarding feature, you must enable X-Forwarding in Putty.
So before you click the "open" button to log on to the remote machine, do this:
- Selete Connection->SSH->X11 on the left column of Putty.
- Choose "Enable X11 forwarding"
- location is:localhost:0
STEP FOUR: Forwarding windows.
Make sure:
- Started Xming.
- Connect to a remote LINUX machine with X11-Forwarding enabled in Putty.
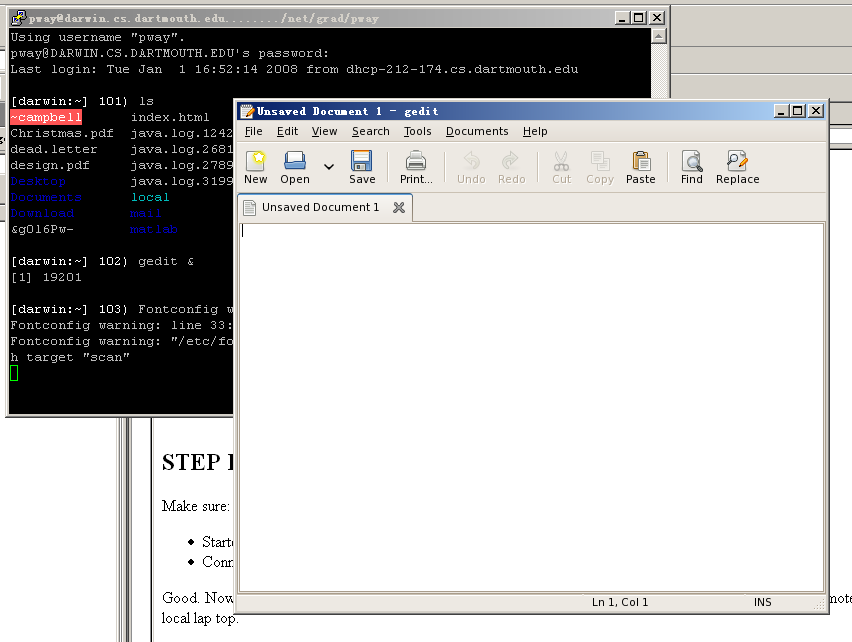
Good. Now type "gedit &" in your Putty text terminal and enter. A
LINUX program will be executed on the remote machine, while its window
is shown on your local lap top.
 X Forwarding
X Forwarding The first ICON is the Xming process.
The first ICON is the Xming process.
