WHAT DOES IT DO?
MIT has developed technology which will channel the various bits and bytes of bio data: a pulse-oximeter to measure blood oxygen, which is a reliable means of testing for hypoxia, an internally carried pill to sample core body temperature measures the potential for hypothermia and send its data via radio signal back to base camp, and a heart rate monitor to measure stress. All of this data will flow back to base camp where the condition of each climber will be carefully monitored. The technology that MIT has created will allow for virtually ongoing data transmission to the website.
HOW DO YOU USE IT?
The beauty of the Biopack is that is easy to use, yet constantly monitors
your condition. You may wonder how complex this equipment is to use given
the conditions. MIT's technology is extremely lightwight and very simply,
as small and unobtrusive as it was possible to make. It all fits in one
neoprene vest and one sensor attaches near the ear. That's it! The vest
automatically records your vital signs and sends the data to a laptop for
monitoring and processing.
WHAT IS HYPOTHERMIA AND HYPOXIA?
Hypothermia is when the core body temperature drops to dangerous levels.
Eventually, the body realizes it cannot save itself and you die. Hypoxia
is the condition which causes the most accidents on the mountain. It
occurs when the oxygen level in the blood drops and leaves you feeling
almost drunk. The danger of hypoxia is that you lose your ability to make
rational decisions. Many deaths on the mountain are due to poor choices
made by hypoxic climbers.
WHAT ELSE CAN IT DO?
The ultimate application for all of this technology is to enable better
quality medical care anywhere, anytime no matter where a patient is in
need. This telemedicine can open a whole new world of care.
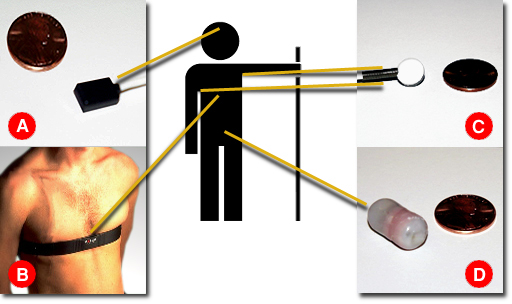
 Nonin blood oxygen sensor - it attaches to the skin near your temple
and measures amount of oxygen
in your blood.
Nonin blood oxygen sensor - it attaches to the skin near your temple
and measures amount of oxygen
in your blood.
 Polar It straps around your chest and
sends your heartbeat to a receiver
Polar It straps around your chest and
sends your heartbeat to a receiver
 Sensor Scientific thermistors - they are stuck under each arm and
measure skin temperature.
Sensor Scientific thermistors - they are stuck under each arm and
measure skin temperature.
 PED Body Core Temperature Monitor (BCTM) - This pill contains a thermometer
and a mini-radio transmitter. It measures your
core body temperature and sends it to a receiver.
PED Body Core Temperature Monitor (BCTM) - This pill contains a thermometer
and a mini-radio transmitter. It measures your
core body temperature and sends it to a receiver.
back.